Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
ICP in 2023: The year of SNS DAOs and Multi-Chain
From groundbreaking Multi-Chain features like ckBTC, ckETH and SNS DAOs to expansive growth in outreach, partnerships and ecosystem projects, 2023 was certainly eventful.
Written by: Angela Harp

While there were many moments that felt like the bear market was going to drag on to oblivion, the ICP community kept pushing forward last year, resilient, focused and incredibly productive. Let’s recap the 2023 highlights, plus get a sneak peak into 2024.
Numbers speak louder than words
Developer growth
2023 was a brutal year for the crypto industry, showing a significant decline in developer activity across top blockchain ecosystems for the first time. The ICP developer community was not immune, but while it lost developers in the first few quarters, the year still closed with a +30% increase despite the slow start. While this growth was mainly driven by part-time developers, it is certainly a precursor for future growth in full-time developers and a sign that the industry is healing, as more developers are gradually returning or joining the ecosystem to explore. Confirming this growth is the fact that the ICP developer community has been moving up the ranks across crypto ecosystems, now in the top five, with a 56% rise in open GitHub repos.
Burned cycles
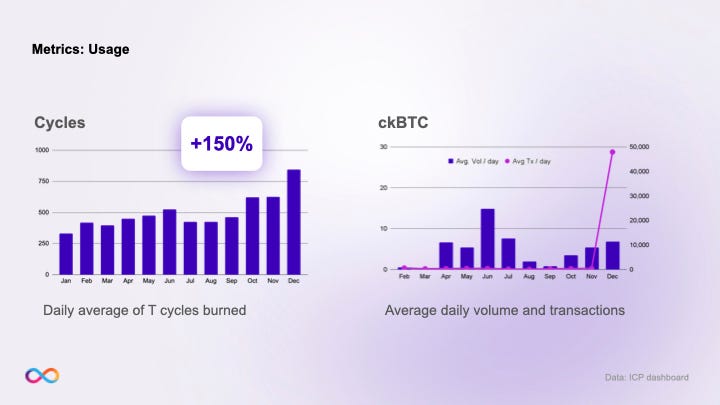
Steadiness in ICP developer growth has also impacted the overall cycle burn rate — a metric that indicates the direct economic value created by the Internet Computer. The daily average of burned cycles continued to rise throughout the year, and the burn rate is expected to triple in January. This was partly due to the rise in ckBTC transactions followed by the recent launch of Bioniq, the new Bitcoin Ordinals marketplace on the Internet Computer. Non-economic activity such as the community experimenting with BRC-20 tokens also contributed to the rise. These are all positive signs pointing to the potential of higher transaction volumes in 2024 as the Multi-Chain functionalities of the Internet Computer continue to evolve.
Topology & hardware upgrades
2023 was a year for mass improvements in node decentralization. With a 67% increase in node providers, the number of countries with node machines has doubled, jumping from 9 to 22. The number of unique data centers also shot up from 40 to 105. In addition to this expansion, new Gen 2 node hardware was introduced to facilitate the future development of features on the Internet Computer. Gen 2 machines support VM memory encryption and attestation.
Overall, improvements and updates to the Internet Computer protocol never ceased to stop. On average, there was roughly one upgrade proposal per day submitted to the NNS DAO. These proposals initiated 88 replica upgrades throughout the year, as well as 352 NNS-controlled canister smart contract upgrades — impressive!

Tokenomics
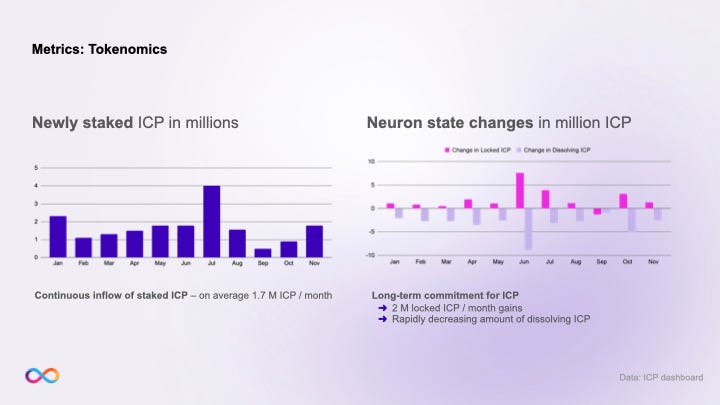
According to the NNS metrics, there was a continuous inflow of staked ICP in 2023, averaging 1.7 million ICP per month coming from new sources. Growth in locked ICP was consistent month after month, except for September, while the amount of dissolving ICP rapidly decreased by the close of the year, which is a good indicator that members participating in governance are showing commitment and are in for the long haul.
ICP in the wild
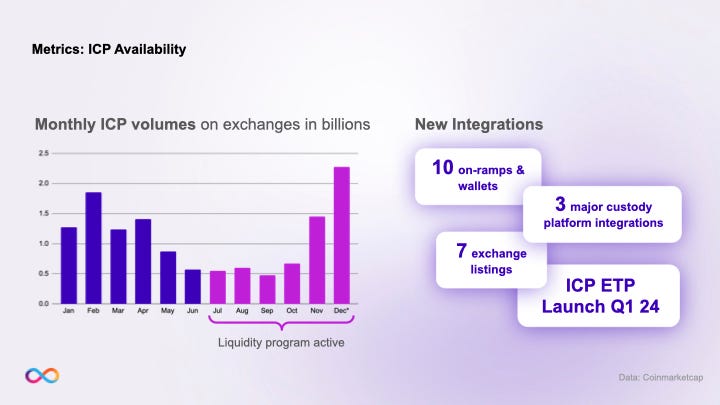
ICP trading on exchanges went up, partly due to the liquidity program introduced mid year as well as several new integrations, including listings on 7 additional exchanges, 10 wallet integrations and 3 major custody platform integrations. Integration rollouts will continue into 2024 with the aim to further increase ICP availability.
Events & outreach
Major marketing efforts to increase global awareness and adoption of the Internet Computer were fueled by an initiative to ramp up activities in three main areas: events (hosting and attending), media and PR, and grassroot adoption through ICP.Hubs. A sprint of in-person events began at the end of the summer, peaking in October, and targeting Asia specifically. In parallel, press mentions and social dominance tripled in comparison to 2022, while ICP.Hubs began popping up in 4 regions in Q3. By Q4, a handful of hubs were fully functioning with focus on developer, entrepreneur and user education and adoption. Today, ICP.Hubs span the Internet Computer’s outreach in 19 regions — an achievement that has stretched the Internet Computer’s community to all corners of the globe. Moving forward, the aim will be to strengthen and refine the synergy between traditional marketing and grassroot efforts.
SNS DAO boom
One of the biggest Internet Computer achievements in 2023 was the launch of the Service Nervous System (SNS) DAO framework. It all began in November 2022 when SNS-1 was released as a test run before the very first OpenChat SNS was officially launched. The year closed with 12 SNS DAO launches, then 2 additional launches after New Year’s, making it 14 in total.
It wasn’t all smooth sailing, however. There were quite a few issues to solve after the feature was released to give users and developers a much better experience. DFINITY R&D teams worked hard throughout 2023 to enhance various aspects of the framework, deploying up to 20 canister upgrades and releasing launchpad improvements such as the one proposal feature, geo restrictions and matched funding. New elements such as predictable swap start times and a testflight modus were also introduced to help developer teams better prepare. And let’s not forget the SNS tools that were also launched to improve the user experience with regard to governance and transparency. Users now have better control over neuron management, and all SNS DAO activity can be monitored on the Internet Computer dashboard.
While DFINITY engineering teams have done a great deal to improve the functionality of the SNS framework, much of feature’s success is due to ecosystem project teams and their determination fully decentralize their dapps as well as the community who have shown support through funding and adapting the various dapps to integrate SNS DAO activity. Not long after the official SNS feature launch, wallets started supporting ICRC-1 tokens — the standard for SNS tokens — and exchanges began trading SNS tokens. Individual dapps such as DSVR, IC Light and OpenChat also rose to the occasion, launching in-dapp features to facilitate SNS DAO voting and governance.
2023 marks the birth of DAOs on the Internet Computer. And while there is still much room for improvement moving forward, the first year of activity hints at a bright SNS future:

ICP 2023 evolution
Since the Internet Computer Genesis in 2021, R&D has been shifting its focus more and more from protocol development to user and use-case centric solutions with the aim to pave the way for easier adoption across industries as well as developer and user communities alike. Take a look at what has evolved in the past year.
Developer experience
As the metrics revealed, it was a tough year for developer growth. Still, much attention was placed this year on improving the developer experience. Perhaps the most important step taken for this initiative was the launch of a developer feedback board. This platform allows ICP developers to more efficiently voice their pain points, make and vote on requests that make building easier. From redesigning the developer documentation portal with emphasis on mapping out a clearer developer journey, to providing targeted sample code and quickstarts that accommodate various skill levels, to introducing new developer tooling, dfx templates, and a playground to simplify the onboarding process, the developer experience is now easier than ever before.
While the focus has shifted towards user-centric solutions, R&D still made massive improvements to the protocol to provide builders with more functionality. One great example was the release of new Wasm instrumentation, which improves the speed of Python and Typescript on the Internet Computer by orders of magnitude. And there is much more to come. Stay tuned for a new cycles ledger soon to be released as well as further improvements to the developer documentation. Anyone with feedback and special requests, be sure to submit them here.
Building a solid L1 for Web3 applications
Early projects teams building on the Internet Computer were attracted by the fact that applications can be built 100% on chain. So in addition to introducing the SNS DAO framework in 2023, R&D teams made several contributions to strengthen the Internet Computer’s decentralized foundation through a number of measures: protocol extensions, new security features, performance and scaling enhancements. Steps were also taken to enable seamless dapp access by removing the service worker and allowing custom domains.
Various performance and scaling improvements were made to accommodate the growth in number of canisters and canister state, both of which increased by 60%! A subnet can now run more than 100k canister smart contracts, for example. And the list of 2023 improvements goes on. From improved stable structures, to increased Wasm-native stable memory, to a subnet splitting MVP, the Internet Computer is ready for expanding applications in 2024.
And as for protocol extensions, one major highlight was the long-awaited release of composite queries, which simplifies the development of multi-canister dapps. The first phase of vetKeys, including a demo and a developer bounty contest, was also released with positive feedback from the ecosystem. This feature enables on-chain encryption, and will be essential for creating a secure and privacy-conscious future for blockchain technology.
Speaking of security — this topic as well as the robustness of the Internet Computer was definitely top-of-mind in 2023, and improvements were made to the replica host OS such that it is now upgradeable through the NNS, allowing faster reaction times to security bots.
Finally, one last highlight worth mentioning — a team of DFINITY researchers submitted a paper to the prestigious USENIX ATC conference, positioning the Internet Computer as a stateful serverless compute platform. The paper gives a detailed analysis of how the Internet Computer can provide serverless computation comparable to existing cloud providers, but with the added benefits of decentralization and statefulness.
Paving the way for a Multi-Chain future
Another big theme in 2023 was cross-chain. DFINITY believes that in the foreseeable future, there will be multiple blockchains, and the Internet Computer, with its unique architecture, is well positioned to capitalize on cross-chain orchestration in the most trustless fashion. The year started out with the launch of ckBTC as a follow-up to the mainnet release of the Bitcoin Integration at the end of 2022. With stable operations throughout the year and no incidents to report, ckBTC and the Bitcoin Integration became a solid building block for the launch of Bioniq, the first Ordinals marketplace on the Internet Computer.
The year then came to a nice close with the launch of ckETH, which enables trustless swaps between BTC/ETH, for example, in seconds for only a few cents and 0 gas fees. 2024 will see more Ethereum multi-chain features with a planned release of an EVM RPC canister, as well as wallet and ERC20 prototypes.
Making the Internet Computer more user-friendly
Whether you’re building dapps, cross-chain solutions or blockchain applications for enterprise, users want to be able to manage their identity, their private keys and their digital assets. This is why DFINITY R&D teams have been focusing on making the Internet Identity onboarding process more user-friendly. A new feature is also underway that supports verified credentials, so users can share private data without revealing who they are.
Wallet prototypes like Oisy, the NNS frontend dapp, token standards for interoperability and custody provider integrations are some of the other areas where R&D teams are exploring ways to create a smoother user experience across the board.
Decentralization is key to building trust
Ultimately, achieving true decentralization will strengthen trust in the Internet Computer. In addition to the topology improvements mentioned above, the NNS DAO adopted a new approach to optimize node onboarding, agreeing that the target topology was reached. In terms of governance, inactive neurons were migrated to a stable storage, which makes the governance system ready for a new wave of neuron holders and ICP stakers.
Trust is also gained through transparency, so the Internet Computer now publicly records node metrics to ensure fair distribution of node rewards.
Infrastructure
The efficiency of engineering teams greatly depends on the underlying infrastructure of the Internet Computer. To this end, various measures were taken to improve speed and robustness, and to streamline processes and reduce costs. For example, merge request pipeline times were reduced by 33%, despite more code being added and more complexity to the code base. This will continue to be an area of improvement in 2024 to make engineering teams more agile.
Dynamic testnets were also introduced to allow a more economical usage of the infrastructure, and to decommission some of the error-prone static testnets. The Internet Computer’s observability stack was then moved to prem, meaning it no longer relies on AWS. This has led to significant cost savings.
Partnerships & test balloons
This year DFINITY engaged in various partnerships around the globe, putting many of the Internet Computer features to the test by building prototypes for real industry use cases. In Dubai, for example, DFINITY joined forces with an international consortium of partners to create a global recycling credit market running on the Internet Computer. The prototype was presented at COP28 last December. In Lugano, Switzerland, the MyLugano city app was extended to support ckBTC payments. Another notable project included the co-creation of a document-sharing prototype with a Swiss private bank. These partnerships and many more not mentioned here illustrate the enormous potential the Internet Computer has to offer solution-oriented blockchain technology to enterprises.
Strengthening the Internet Computer ecosystem
The main mission of the Growth team at DFINITY is to attract and support innovative developer teams to build on the Internet Computer, while enhancing the quality and alignment of projects in the ecosystem, and helping them succeed. In 2023, the team’s priority was to scout out more strong entrepreneur-minded developers by organizing activities such as bootcamps, hackathons and industry partnerships.
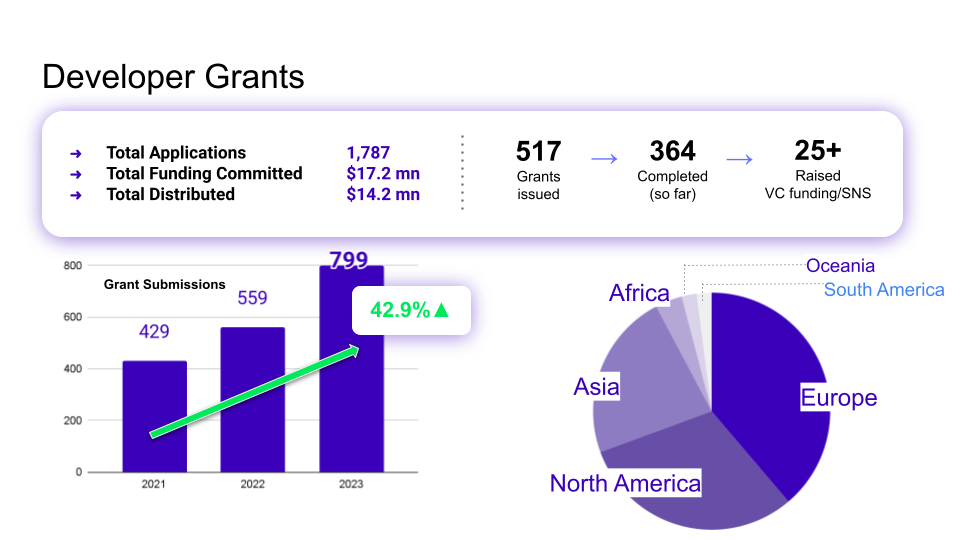
In addition to organizing developer events and partnering with external institutions such as the Bitcoin Startup lab on hackathons, bounties and contests were focused or themed around core Internet Computer capabilities, such as Bitcoin Integration or GameFi. Winners were then mentored and encouraged to build on the Internet Computer, and selected hackathon winners with promising projects were also given grants with the aim to bring them into the ecosystem, nurture them and partner with them. To give some perspective on grants, DFINITY committed $17.2 mn last year, $14.2 mn of which was disturbed across the 517 grants issued globally. Grant submissions increased by 42.9%, partially due to increased grassroot activities around the regional ICP.Hubs. Some recent grantee projects worth mentioning include Nostric, ICP Canister Bridge and LOKA.
For projects already in the ecosystem, quarterly ICP.Labs events are held to bring ecosystem teams and DFINITY R&D teams together around specific themes and topics, as well as to foster collaboration, share best practices and address blockers and pain points. And finally, 2023 was all about ramping up requests for startups, launching targeted bounties to encourage ICP developers to experiment with top Internet Computer features, and supporting successful projects through marketing and PR opportunities. These initiatives will remain in strong focus throughout 2024.
Moving forward, it will require continuous exploration to find the right mechanism that attracts top entrepreneurs and developers. It will also take a strong collaborative effort to identify what the current gaps are in order to unblock any obstacle that stands in the way of any given project’s success.
Global marketing & adoption initiatives
Last but not the least, the DFINITY Global Marketing & Adoption team has taken massive strides to build and maintain a vibrant ICP community of developers, users, entrepreneurial partners and enthusiasts. Running with the message that the Internet Computer is not just an innovation, but also a beacon of global transformation, the team’s mission is multifaceted. From marketing and promotional activities to community engagement and events, to partnership development, educational initiatives and market analysis, strategies were formed to bring awareness and adoption of the Internet Computer to new heights around the globe.
Some notable highlights in 2023 include showcasing the Internet Computer at more than 270 events both within Web3 and Web2 space, 70+ collaborations such as FederItaly, Roland Berger and the Municipality of Lugano, and more than 180 education initiatives with universities and online learning platforms across the globe. PR also skyrocketed this year with media coverage on ecosystem projects, AI initiatives, partnerships and more. Finally, the ICP.Hubs program was launched in Q3, starting with 4 hubs, and ending with 19 at the close of the year, and 4 more in the pipeline for 2024. This program is a grassroots effort that supports local communities in actively establishing hubs to promote awareness and adoption of the Internet Computer through evangelism, education, strategic partnerships, and project acceleration.
A peak into 2024
2023 was full of action but we’re not even close to being done yet. There’s a whole lot more in store for 2024!!
Here’s a sneak preview of some of the features R&D has in the pipeline:
- Decentralized boundary nodes: aims at bringing routing messaging under NNS control to make it fully decentralized.
- EVM RPC: enables smart contract on ICP to call out to smart contracts on EVM chains (initially on Ethereum mainnet, and later to L2s and other EVM chains)
- Improved orthogonal persistence for Motoko: more memory to Motoko and faster upgrades to Motoko canisters.
- Canister snapshots
- Canister logging
- Large WASM module installation
- Libraries for certification: new libraries planned to make the developer experience more user friendly.
- ckERC20, ckUSDT & ckUSDC: introduce generic ERC tokens to ICP to boost DeFi with fiat-backed stablecoins.
- Threshold Schnorr: introduce threshold signing for Schnorr-based signatures to support taproot transactions needed for Ordinals as well as non-EVM ecosystems like Solana and Cardano.
- Credential support for Internet Identity
- More storage capacity on subnets
- Subnet rental: enables ICP to create subnets that are exclusively used (and paid for) by individual projects.
- On-chain encryption: continue with the next phase of the vetKeys feature to enable ICP dapps to securely derive cryptographic keys that can be used to encrypt and decrypt user data.
Be sure to stay in the loop on the ICP Developer Forum or DFINITY Dev X. It’s going to be another exciting year!
Watch the 2023 highlights on YouTube:
Learn more about the Internet Computer:
Dev X | Dev Forum | YouTube | GitHub | Developers Center | Discord
ICP in 2023: The year of SNS DAOs and X-chain was originally published in The Internet Computer Review on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.