Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
Assessing the Risk Landscape of Ethena’s Synthetic Stablecoin And Its Yield Revolution

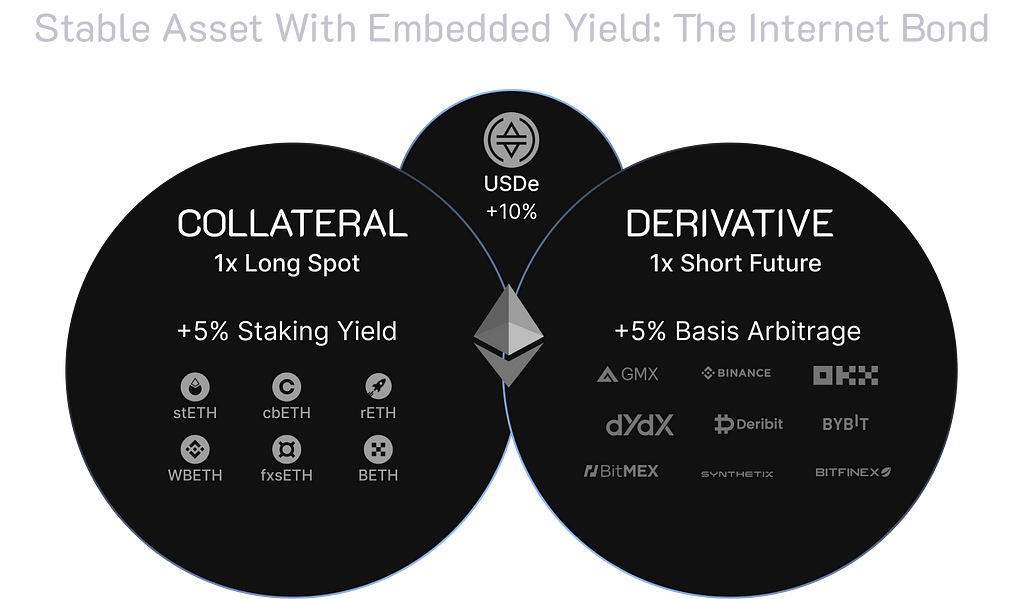
Ethena Labs launched their synthetic dollar coin called USDe on Ethereum, along with a dollar-denominated savings instrument known as the “Internet Bond.” Ethena has achieved outstanding growth, reaching $2.24B of TVL since mid December 2023. Unlike traditional fiat stablecoins like USDC or USDT, USDe is fully collateralized with crypto assets and its corresponding short futures positions.
USDe aims to provide a censorship-resistant, scalable, and stable crypto-native solution, not reliant on the traditional banking system. It is fully backed on-chain and can be freely composed throughout the DeFi ecosystem. The peg stability of USDe is maintained through delta-hedging mechanism, using staked Ethereum collateral against protocol-held derivatives short positions.
Their main product called the Internet Bond combines yield from staked Ethereum with funding and basis spread from perpetual and futures markets. This creates an on-chain crypto-native ‘bond’ that can serve as a dollar-denominated savings instrument. This initiative addresses the fragility and scalability issues faced by current decentralized stablecoins, marking a significant leap towards achieving a functional decentralized financial system.
sUSDe Yield Is The Byproduct Of Basis Trading
The USDe yield source mainly comes from two strategy legs. First, their spot ETH exposure, earning the staking yield that has lately been oscillating between 3–5% APR. Secondly, the net yield must include the funding yield received from opening and maintaining short positions on futures contracts of ETH. In the current bullish market sentiment, the majority of the positions are long, so they pay a large funding rate to their counterparty short positions, which Ethena takes. These two legs allow the positions to be delta-neutral, so any ETH price variation is mitigated since both positions are hedged. This is what is known as a basis trade, though this is typically executed with traditional futures contracts instead of perpetual swaps.
Ethena’s Documentation
By utilizing derivatives on staked Ethereum collateral via deep, liquid centralized venues, USDe aims to solve the “stablecoin trilemma’’ of scalability, stability and decentralization. The Internet Bond can provide an uncensorable, trustless native yield at scale, combining the stability of stablecoins with the censorship resistance of staked ETH. Further plans of Ethena to achieve scalability through capacity expansion is to support BTC basis trade as well.
Risks to Consider
While Ethena’s yield is compelling currently at over 25% APY, there are significant risks to be aware of:
- Smart contract risk — As with any DeFi protocol, bugs or exploits in the smart contract code could lead to loss of funds.
- Collateral risk — USDe is backed by staked ETH (stETH). If the value of stETH were to significantly decrease, it could cause issues in maintaining the USDe peg.
- Futures/derivatives risk — The delta-hedging mechanism relies on short futures positions. Unexpected volatility or issues with these derivatives markets could destabilize the peg. Moreover, since spot and futures are traded separately, their prices are not guaranteed to be the same at all times, so maintaining an equal net position between both trading legs is a challenge. Executions and rebalancing costs are important factors to consider in a basis trade.
- Regulatory risk — Evolving regulations around crypto, derivatives, and securities could impact the protocol and accessibility of the Internet Bond.
- Operational risk — Ethena Labs will need to execute their complex design effectively. Any failures in deployment or operations are a technical risk.
Ethena’s Economic Stability
Understanding the risk profile of a synthetic dollar protocol such as Ethena’s USDe is critical for investors, users, and the broader DeFi ecosystem. Ethena’s USDe, a synthetic dollar collateralized with crypto assets and corresponding short futures positions, presents a unique risk landscape compared to traditional fiat stablecoins. These integrated data visualizations provide a comprehensive risk assessment tool, crucial for evaluating the protocol’s health, performance, and stability.
USDe Value Stability: A Core Consideration
A key metric for any stablecoin, including Ethena’s USDe, is its peg stability. The data indicate that USDe’s peg stability mechanism, delta hedging staked Ethereum collateral, is effectively maintaining its synthetic dollar value. Stability is a primary indicator of reduced risk in the protocol’s operation, ensuring that USDe can be reliably used for transactions, savings, and as a reference in DeFi applications.
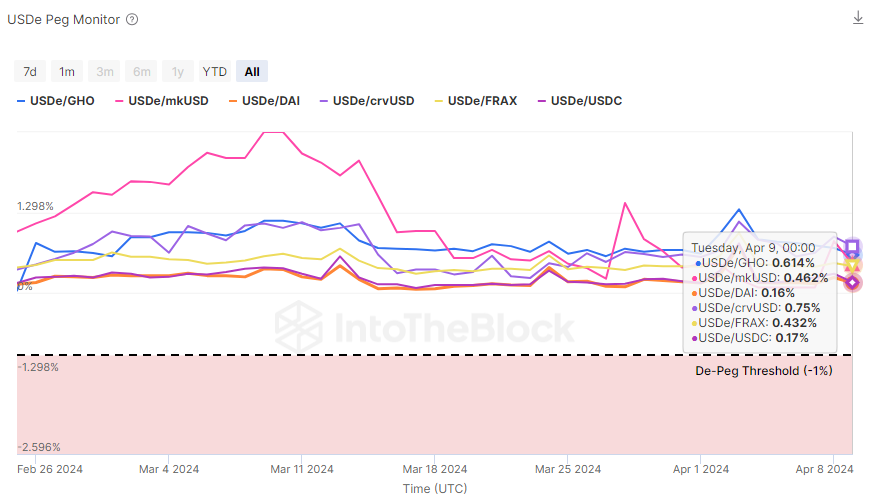
USDe Peg Monitor Indicator
As can be shown in the chart above, USDe has been trading without reaching any price depegs in its most liquid DEX pool on Curve, with $30M of liquidity. It has been trading tightly within a ±1.00%, showing strong monetary stability as a synthetic stablecoin. This metric can more easily keep track of it with a heatmap that shows depegs over time:
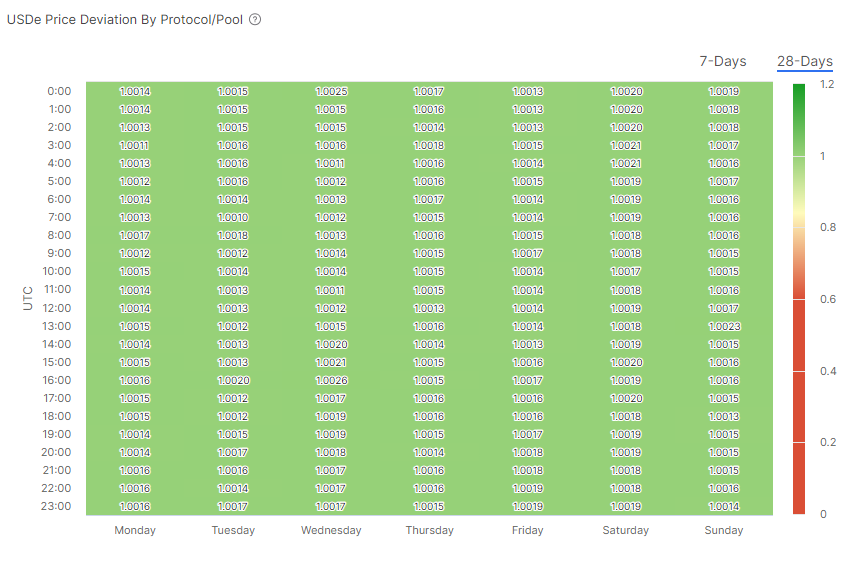
USDe Price Deviation Chart
Monitoring Curve pools dynamics can be a leading indicator of potential price depegs. This is due to how Curve pools work. Curve pools can stay imbalanced on one of their assets until a certain point, where their invariant curve changes behavior rapidly due to their amplification factor, where subsequent trades could affect price divergences more severely. That is why is a good practice to monitor the asset balance of the pool, taking note in consistent trends over time of imbalances:
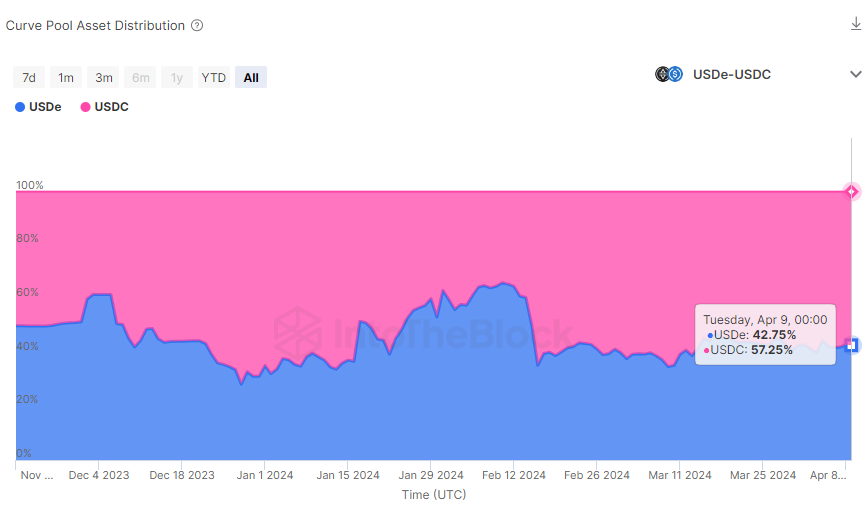
USDe Curve’s pool asset distribution
As seen in the chart above, the pool asset distribution has been oscillating naturally between a 30–70% asset distribution over time, far from the turning point of a pool with an amplification factor of 200, where large price imbalances occur at distributions closer towards a 5%-95% distribution. If the pool would keep such a drastic distribution over a prolonged period of time then it would be handy to keep an eye on further trades that could largely imbalance further the pool and exacerbate price depegs.
Under such circumstances where a price depeg could trigger a large amount of USDe to be exchanged for USDC, the pool shows resiliency, allowing half of the liquidity of the pool to be exchanged for USDC and withdrawn for only a exit fee impact of 2.26% for an existing position size of 5% of the pool. This is originated from the price impact of imbalancing further the pool.
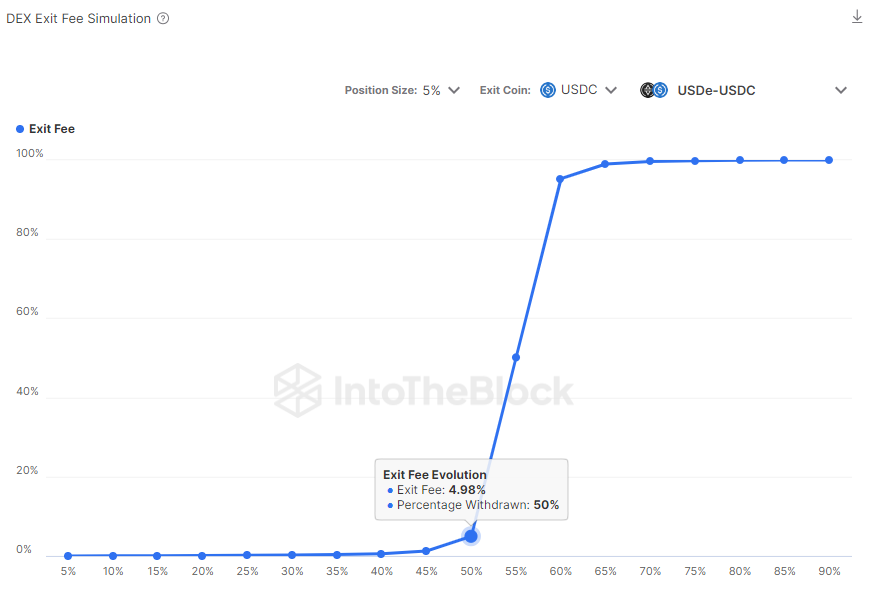
DEX Exit Fee Simulation
A hypothetical future situation of a worse pool asset distribution would move the inflection point more towards the 5–15% area, where monitoring liquidity flows becomes critical to prevent further price depegs.
Liquidity Is The Main Door
Ethena’s minting mechanism allows whitelisted market makers to mint and redeem USDe with supported collaterals, while non-whitelisted/regular users can access to USDe by buying it through external liquidity pools. In case USDe holders want to exit the Ethena ecosystem, it is expected that the whitelisted parties would redeem their collateral for the USDe they hold, not impacting the markets where USDe trades, but regular users would have to swap through DEX pools in order to exchange back to other stables. This is why it is healthy to maintain ample liquidity for USDe relative to its market capitalization, currently at $1.7B.
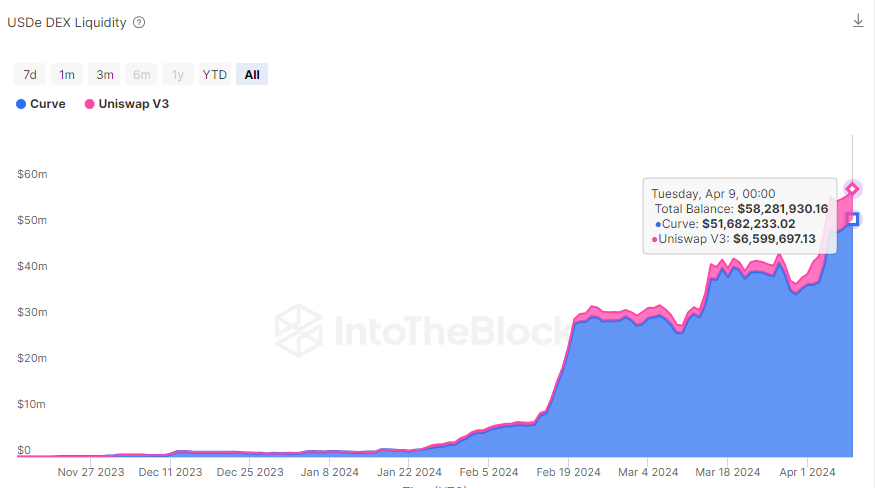
USDe DEX Liquidity
As seen in the chart above, the DEX liquidity of Ethena’s Stablecoin is at $50–60M. Although this a low number, around a 3% of their total market capitalization, it is expected that whitelisted market-makers (which are large holders of USDe supply) would aid in a potential USDe depeg situation. They would absorb a large portion of a potential selling supply of USDe, which in case that would trade at a discount would allow these parties to acquire it (improving its peg) and redeem it for their ETH collateral, profiting from the arbitrage and restoring the price stability of USDe in that case. This is why a dynamic mint and redeem mechanic combined with frequent arbitrages are key for the stability of the protocol.
Arbitrage Means Stability
As shown in the charts below, the arbitrage ecosystem of Ethena is very active at the moment, with frequent arbitrage transactions daily, some days peaking at more than 100 arbitrage transactions, which some days can profit up to $100k in total.
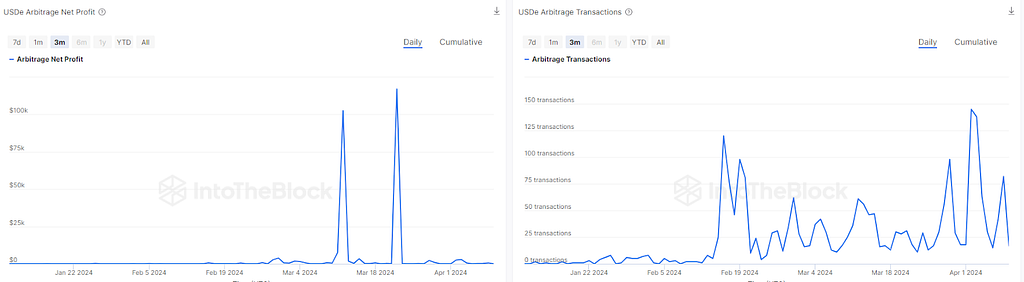
USDe Arbitrage profits and transactions charts.
This ensures that price divergences of USDe are absorbed correctly, increasing the USDe supply through its minting mechanism when USDe trades above peg, being able to deposit ETH and receive a larger amount of USDe in dollar terms than the value of the ETH deposited, when the USDe is sold.
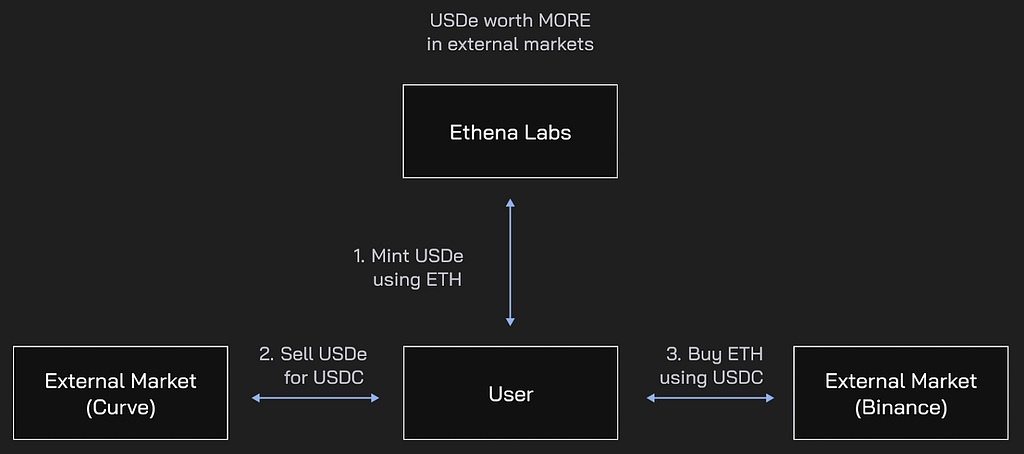
Ethena Documentation
Likewise decreasing the USDe supply is done through the redeeming mechanism when USDe can be acquired below its price peg, receiving a larger amount of ETH collateral in dollar terms than the value of USDe acquired at discount in dollar terms, and selling that ETH for profit. This is what is known as the Peg Arbitrage Mechanism.
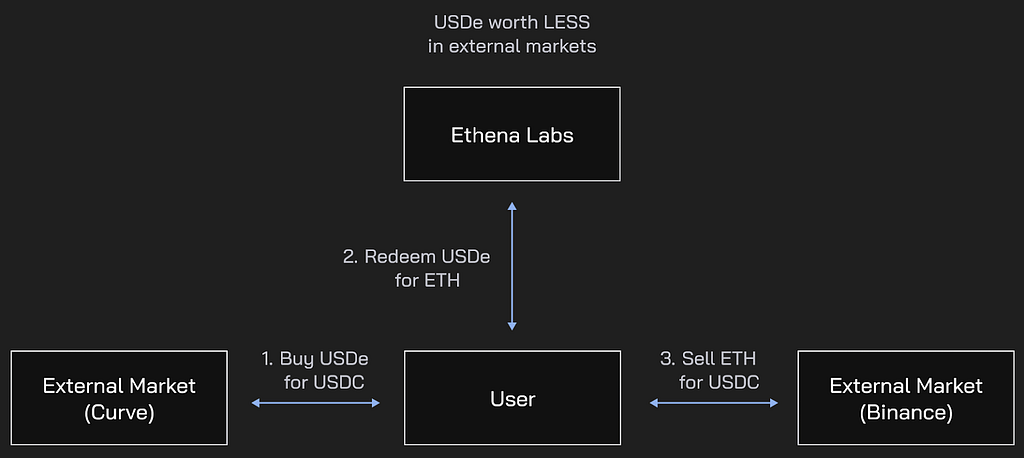
Ethena Documentation
The Reserve Fund As The Last Resort
The reserve fund is a financial reserve maintained by Ethena Labs to mitigate the potential risks associated with negative funding rates in their derivatives positions, such as perpetual contracts. The reserve fund steps in when the combined yield between the LST asset (e.g., stETH) and the funding rate for a short perpetual position is negative, ensuring that the collateral underpinning USDe remains unaffected and that users who stake their USDe for sUSDe do not experience any negative yield.
At over $30M of funds currently, monitoring the reserve fund is crucial for preventing risk because it acts as a buffer against the potential impact of persistently negative funding rates. Although historical data suggests that negative funding rates tend to revert to a positive mean and do not persist for extended periods, the reserve fund provides an additional layer of protection.
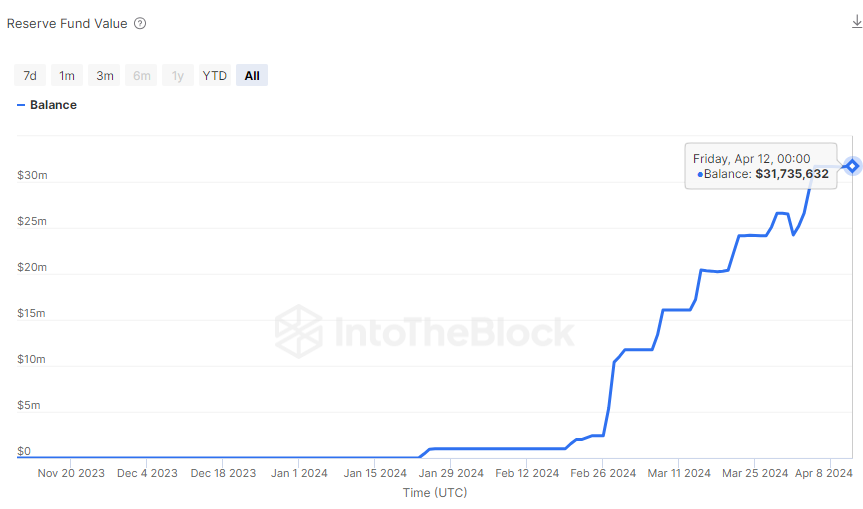
Reserve Fund Value Chart
By closely tracking the reserve fund’s balance and the frequency and duration of negative funding rate occurrences, Ethena Labs can ensure that the fund remains adequately capitalized to cover any temporary losses and maintain the stability of the USDe stablecoin and the overall protocol. If the current fund value is taken and certain negative funding rate situations are considered an extrapolation can be created marking how much the funding rate would last:
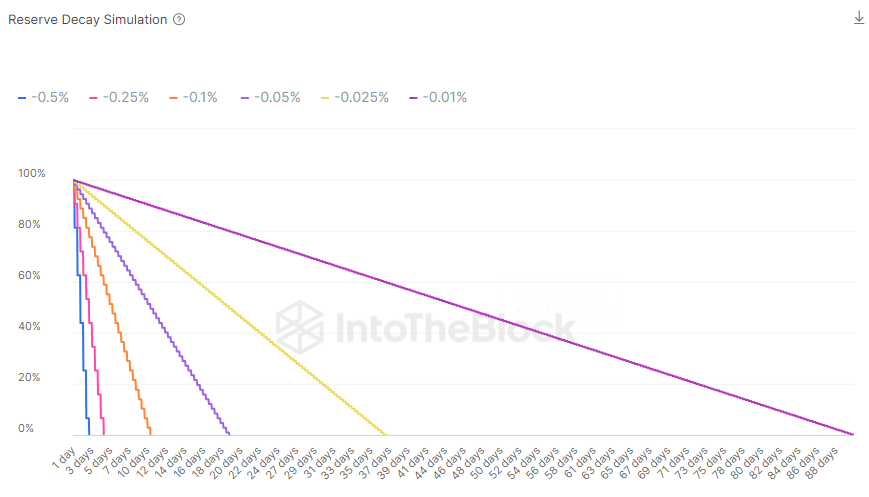
Reserve Decay Simulation Chart
In order to continue increasing the fund value Ethena is committed to send the value accrual from the Protocol backing assets attributable to the portion of USDe that has not been staked, which currently is at 73% of the total USDe supply. A value that is understandable due to the incentives that are distributed among several DeFi protocols to use pure USDe instead of its staking coin sUSDe. For context, ETH historical funding rates have oscillated in the last year to a maximum of -0.05% over the past year, which would be equivalent to 20 days for the reserve fund to be used.
In conclusion, Ethena Labs’ innovative approach with the introduction of USDe and the Internet Bond, presents a forward-thinking solution to the challenges faced by traditional and decentralized stablecoins. Their strategy not only seeks to address the stablecoin trilemma of scalability, stability, and decentralization but also provides a viable, yield-generating alternative for investors in DeFi. The data and charts provided herein offer a visual representation of USDe’s stability, the robustness of its peg mechanism, and the liquidity dynamics that play a crucial role in its operational success. Keeping an eye on these charts can help investors to understand leading economic risks that could arise in cases of unfavour market conditions.
As the DeFi landscape continues to evolve, the role of synthetic stablecoins and yield-generating instruments like the Internet Bond will undoubtedly grow in significance. Ethena Labs has positioned itself at the forefront of this evolution, leveraging deep liquidity, innovative financial mechanisms, and a clear commitment to transparency and risk management. For those interested in exploring the detailed mechanics of USDe, the Internet Bond, or the broader implications of Ethena Labs’ contributions to the DeFi ecosystem, visiting our IntoTheBlock Risk Radar Dashboard is highly recommended. In our Risk Radar, users can find comprehensive risk assessments that provide actionable insights for potential economic risk mitigations on most of the predominant DeFi protocols in the space.
. . .
About the IntoTheBlock DeFi Risk Radar
IntoTheBlock’s newly launched DeFi Risk Radar is a sophisticated tool for institutional-grade risk management in the DeFi sector. Developed through rigorous testing and partnerships, it addresses the significant economic risks within DeFi that have contributed to nearly $60 billion in losses.
The Risk Radar today supports fourteen key DeFi protocols and offers tailored economic risk metrics, high data granularity, an intuitive API and CSV data download functionality. IntoTheBlock’s expertise, gained from years of working with the largest institutions in crypto, strengthened the development of this tool, aimed at enhancing risk analysis and management in the DeFi markets. Additionally, we expect to release more protocols in 2024, expanding the scope and efficacy of our risk management solution.
If you want to know more about Risk in DeFi, We recommend downloading our latest report, which explores DeFi risk in detail.
Navigating Risks and Innovations with Ethena’s Synthetic Stablecoin was originally published in IntoTheBlock on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.